BMI Calculator
Personal Recommendations
Struggling to understand whether your weight is in a healthy range? Many people worry about being overweight, underweight, or at risk for serious health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure—but figuring it out can be confusing.
The BMI Calculator is a simple yet effective tool that helps you assess your Body Mass Index (BMI) based on your height and weight, giving you a clear idea of where you stand.
Whether you’re aiming for weight loss, muscle gain, or just maintaining a healthy lifestyle, understanding BMI can help you make informed decisions about your health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down how BMI is calculated, its accuracy, its limitations, and what your BMI number means for your overall well-being.
What is BMI?
Definition of Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used numerical value that helps determine whether a person’s weight is appropriate for their height. It is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms (kg) by the square of their height in meters (m²).
The result categorizes individuals into underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese groups, helping assess potential health risks related to weight.
Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet introduced the BMI formula in the 19th century as part of the Quetelet Index. Today, it is widely used by health professionals, researchers, and organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as a standard screening tool for weight-related health issues.
Why is BMI Important?
BMI is a simple, fast, and cost-effective way to assess weight status and determine whether a person is at risk for chronic health conditions. While BMI does not measure body fat percentage or muscle composition, it serves as a useful indicator for evaluating overall health risks.
Health Risks Associated with an Abnormal BMI
Having a BMI that falls outside the normal range may indicate a higher risk of developing serious medical conditions, including:
While BMI is a useful screening tool, it does not differentiate between muscle and fat, making it less accurate for athletes and older adults, so it should be used alongside other health assessments like body fat percentage, waist circumference, and lifestyle factors for a clearer picture of overall health.
How to Calculate Body Mass Index (BMI)?
Calculating Body Mass Index (BMI) is straightforward and requires only two basic measurements: weight and height.
BMI provides an estimate of body fat levels and helps determine whether an individual falls within a healthy weight range.
While the basic formula remains the same, it is calculated differently in the metric system (kilograms and meters) and the imperial system (pounds and inches).
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate BMI
Step 1: Measure Your Weight
Step 2: Measure Your Height
Step 3: Apply the BMI Formula
BMI Formulas
Metric System (Standard Formula)
For those using kilograms and meters, the BMI formula is:
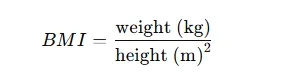
Example Calculation (Metric System)
BMI Result: 22.9 (Rounded) → Healthy weight
Imperial System (U.S. Formula)
For those using pounds and inches, the BMI formula is:
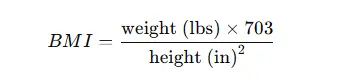
Example Calculation (Imperial System)
BMI Result: 22.7 → Healthy weight
How to Calculate Adult BMI?
For adults (ages 20 and older), BMI is categorized into the following weight classifications:
- Underweight: BMI below 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obesity: BMI of 30 or higher
Limitations of Adult BMI
While BMI is an effective screening tool, it has limitations:
- Does not differentiate muscle from fat – Athletes with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but not be overweight.
- Does not consider fat distribution – BMI does not measure where fat is stored (e.g., abdominal fat vs. fat in the lower body).
- Not suitable for all populations – Older adults and people with high bone density may have misleading BMI results.
How to Calculate Child and Teen BMI?
For children and teenagers (ages 2–19), BMI is calculated the same way as for adults but is interpreted differently. Instead of fixed categories, BMI-for-age percentiles are used based on a child's age and sex.
BMI-for-Age Percentiles (CDC Growth Charts)
- Underweight: Below the 5th percentile
- Healthy weight: 5th to 85th percentile
- Overweight: 85th to 95th percentile
- Obesity: 95th percentile or higher
Why BMI Percentiles for Kids?
Children’s BMI varies as they grow. Using BMI percentiles accounts for natural differences in body fat at different ages and between boys and girls.
Health Risk Classification According to Body Mass Index
The table below outlines BMI categories and associated health risks:
| BMI Category | BMI Range (kg/m²) | Health Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Below 18.5 | Increased risk of malnutrition, osteoporosis, and weakened immune system |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 – 24.9 | Low health risk |
| Overweight | 25.0 – 29.9 | Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes |
| Obesity (Class I) | 30.0 – 34.9 | High risk of heart disease, stroke, and metabolic disorders |
| Obesity (Class II) | 35.0 – 39.9 | Very high risk of severe health complications |
| Obesity (Class III) | 40.0 and above | Extreme risk of life-threatening conditions |
Final Verdict
The BMI Calculator is a simple and effective tool for assessing weight status and potential health risks. However, while it provides a general guideline, it is not a perfect measure of body fat or health. Factors like muscle mass, fat distribution, and overall body composition should also be considered.
Key Takeaways
- BMI is an important health indicator but should not be used in isolation.
- A high BMI may indicate obesity-related health risks, but additional tests (body fat percentage, waist circumference) can provide a more accurate health assessment.
- For children and teens, BMI should be evaluated using percentiles based on age and sex.
- Healthy lifestyle choices—including balanced nutrition and regular exercise—are crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
By using the BMI Calculator, you can take the first step in understanding your weight status and making informed health decisions. If your BMI falls outside the normal range, consider speaking with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
