Loan Calculator
Calculate your monthly payment and view your loan details.
| Payment # | Principal | Interest | Total Payment | Remaining Balance |
|---|
Borrowing money can be a daunting journey, often clouded by concerns about affordability, unexpected fees, and the complexities of long-term financial planning.
Many borrowers struggle to understand repayment terms, navigate fluctuating interest rates, or anticipate total loan costs, leading to financial stress and uncertainty.
Our advanced loan calculator is specifically designed to tackle these issues, offering instant and accurate breakdowns of monthly payments, total interest, and repayment schedules.
By providing clear and actionable insights, our tool empowers you to make well-informed financial decisions, ensuring transparency, affordability, and peace of mind every step of the way.
How to Calculate a Loan with Our Tool?
Our loan calculator makes it easy to determine your monthly payments, total repayment amount, and interest costs. Follow these steps:
- Enter Loan Amount: Input the total amount you plan to borrow, like $100,000 for a home loan.
- Specify Interest Rate: Add the annual interest rate (e.g., 5% as "5"). This reflects the cost of borrowing.
- Set Loan Term: Select the repayment period in years, such as 30 years for a mortgage or 5 years for a car loan.
- Add Extra Payments (Optional): If you want to pay off the loan faster, include an additional monthly payment, like $300.
- Click Calculate: Instantly see a detailed breakdown, including monthly payments, total interest, and a full payment schedule.
Example Calculation
For a $100,000 loan at 5% interest over 30 years with $300 extra monthly payments:
This calculation includes a month-by-month breakdown, showing how each payment reduces your balance while covering interest.
Our tool ensures accuracy, saves time, and helps you plan your finances confidently. Try it now to see how much you can save!
How to Calculate a Loan Manually?
Manually calculating a loan involves understanding the formula for monthly payments and carefully applying it step by step.
Although this process requires basic math skills and attention to detail, it can provide a clear picture of your loan terms. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
Step 1: Understand the Formula
The formula for calculating the monthly payment on a loan is:
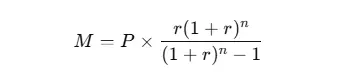
Where:
For example, if you’re borrowing $100,000 with an annual interest rate of 5% over 30 years, you’ll calculate your monthly payment as follows.
Step 2: Plug in the Values
Let’s break it down using the example loan details:
Step 3: Perform the Calculations
Step 3.1: Calculate (1+r)n(1 + r)^n(1+r)n
Add 1 to the monthly interest rate:
Raise this value to the power of the total number of payments:
Step 3.2: Multiply by the Monthly Interest Rate
Multiply the result by r:
Step 3.3: Subtract 1 from (1+r)^n
Step 3.4: Divide the Results
Divide the result from Step 3.2 by the result from Step 3.3:
Step 3.5: Multiply by the Loan Amount
Finally, multiply this value by the principal amount P:
The monthly payment is approximately $494.
Step 4: Calculate Total Payments and Interest
Step 4.1: Total Payments
Multiply the monthly payment by the total number of payments:
This is the total amount you’ll repay over the loan term.
Step 4.2: Total Interest
Subtract the original loan amount from the total payments:
The total interest paid over 30 years is $77,840.
Final Verdict
Financial calculations for loans require meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of compound interest mechanics.
The provided analysis demonstrates that for a standard $100,000 loan with a 5% annual percentage rate (APR) over a 30-year amortization period, borrowers can expect monthly installments of approximately $494, culminating in total payments of $177,840 throughout the loan tenure.
This results in a cumulative interest burden of $77,840, highlighting the significant impact of compound interest over extended repayment periods.
The mathematical formula M = P × r (1 + r)ⁿ/(1 + r)ⁿ-1 serves as the fundamental calculation engine, where the principal (P), monthly interest rate (r), and payment periods (n) interact to determine the monthly obligation.
Whether using manual calculations or automated tools, understanding these financial metrics - including amortization schedules, principal reduction, interest accrual, and total cost of borrowing - is crucial for making informed lending decisions and maintaining fiscal responsibility throughout the debt lifecycle.
